NSX-T Multi Site
 |
| NSX T Multi Site Topology |
The above topology is for NSX-T Multi Site.
1. There are two Tier 0 Gateways provisioned.
One Tier 0 Gateway is in Primary Site.
The other Tier 0 Gateway is in DR site.
2. There is one DR only Tier 1 Gateway to which segments are connected.
Workload VMs are connected to these segments.
Tier 1 Gateway serves as the gateway for the workload VMs.
Tier 1 Gateway is connected to Tier 0 Gateway of Site 1.
3. Vcenter server and NSX-T Manager Cluster is on the stretched management cluster and the cluster is protected by vSphere HA.
4. Management network in which the vcenter server and NSX-T managers reside is stretched across both the sites.
This facilitates automatic recovery of management plane upon failure of Primary Site.
5. Segments are stretched across both the sites as a result there is stretched Layer 2 between both sites.
Workload VMs can vmotion across to the other site keeping the same IP address and the same Distributed Firewall security policy.
6. Two NSX-T Edge Clusters are present, one in each site.
Tier 0 Gateway of Site 1 uses the edge cluster of Site 1.
Likewise, Tier 0 Gateway of Site 2 uses the edge cluster of Site 2.
NSX-T Fabric Details:
 |
| Transport Zones |
Two VLAN backed transport zones are used for North-South peering between NSX edges and the physical routers.
Since the edges are using N-VDS on compute hosts for connectivity, a VLAN backed transport zone will be associated with compute hosts.
Separate subnets have been used for edge TEPs and TEPs on compute hosts.
 | |||
| Uplink Profiles |
a. Edges in Site 1
b. Edges in Site 2
c. Compute hosts in Site 1
d. Compute hosts in Site 2
 |
| Compute TEP Pool Site 1 |
 |
| Compute TEP Pool Site 2 |
 |
| Edge TEP Pool Site 1 |
 |
| Edge TEP Pool Site 2 |
a. TEP Pool for compute hosts in Site 1
b. TEP Pool for compute hosts in Site 2
c. TEP Pool for edge transport nodes in Site 1
d. TEP Pool for edge transport nodes in Site 2
 |
| Trunk Segments for connectivity of Edges |
 |
| Segments for uplink interfaces on Tier 0 Gateway of Site 1 |
 |
| Segments for uplink interfaces on Tier 0 Gateway of Site 2 |
These segments are used while creating uplink interfaces on Tier 0 Gateway.
Two segments are required for Tier 0 Gateway in Site 1.
Likewise two more segments are required for Tier 0 Gateway in Site 2.
 |
| Edge Transport Nodes and Transport Zone Association |
 |
| Compute Transport Nodes and Transport Zone Association |
Transport Zone Association:
- Hosts have transport zone ESXi as VLAN backed transport zone and Overlay transport zone associated.
- Edges have Overlay transport zones in addition to VLAN backed transport zones.
 |
| Host Transport Node Configuration in Site 1 |
Compute TEP subnets are different in Site 1 and Site 2.
 |
| Host Transport Node Configuration in Site 2 |
 |
| Edge Transport Node Configuration – Site 1 – EN 1 |
 |
| Edge Transport Node Configuration Site 2 – EN 3 |
The edge transport nodes are configured.
Trunk segments created on N-VDS of compute hosts are used as uplinks on the edges.
Appropriate uplink profiles and TEP pools are used.
Two different subnets are used for edge TEP interfaces in the two sites.
 |
| Edge Cluster in Site 1 |
 |
| Edge Cluster in Site 2 |
- One edge cluster for Tier 0 Gateway in Site 1
- Second edge cluster for Tier 0 Gateway in Site 2
 |
| Tier 0 Gateway in Site 1 |
 |
| Tier 0 Gateway in Site 2 |
 |
| Layer 3 interfaces on Tier 0 Gateway of Site 1 |
 |
| Layer 3 interfaces on Tier 0 Gateway of Site 2 |
- Tier 0 Gateway in Site 1
- Another Tier 0 Gateway in Site 2
Layer 3 interfaces are then created as above on each of the Tier 0 Gateway.
BGP Setup and routing configurations:
 |
| BGP Diagram |
e BGP peering is used between edges and the physical routers.
BGP AS number 65000 is used within NSX and BGP AS number 65001 is used in the physical network.
The physical routers are sending default route towards the edges.
Routers in the physical network are configured with loopback networks
- 172.30.1.1 is loopback on physical router 1
- 172.30.2.2 is loopback on physical router 2
- 172.30.3.3 is loopback on physical router 3
- 172.30.4.4 is loopback on physical router 4
Physical routers 1 and 2 are in Site 1
Physical routers 3 and 4 are in Site 2
Full mesh i BGP is used between the physical routers in this lab setup.
Usage of route reflectors is recommended in production networks instead of a full meshed i BGP setup to reduce the number of i BGP peerings, also to optimize physical router resources.
North South traffic flow under normal operations is through Primary Site 1.
Tier 1 Gateway is connected to Tier 0 Gateway of Site 1 during normal operations.
 |
| Setup BGP AS number on Tier 0 Gateway |
 |
| BGP peers on Tier 0 Gateway of Site 1 |
Here BGP AS number is defined.
And also appropriate BGP peers are defined.
 |
| Advertise connected subnets on Tier 1 Gateway |
 |
| Redistribution settings on Tier 0 Gateway of Site 1 |
 |
| Redistribution settings on Tier 0 Gateway of Site 2 |
Traffic Flows during normal operations
 |
| Traffic flow during normal operations through Primary Site 1 |
Under normal operations, North South traffic flow will be through Site 1/Primary Site as shown above.
 |
| Routing table on Tier 0 SR on Edge Node 1 - Site 1 |
This Tier 0 SR is learning default routes from upstream physical routers.
It is also learning the loopback networks defined on each physical routers because those are advertised via BGP.
 |
| VM on segment is able to reach the loopback networks on physical routers |
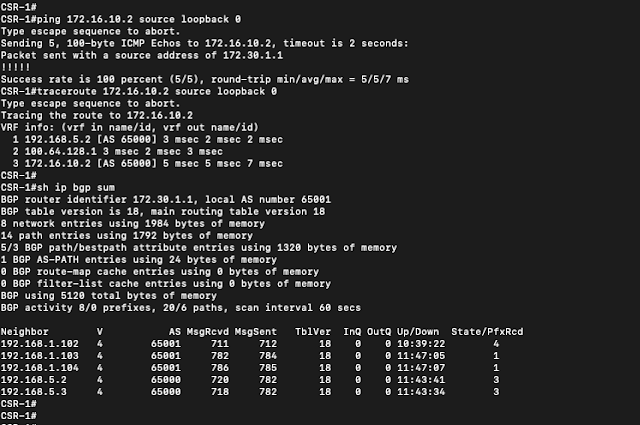 |
| Trace from Site 1 physical router to VM on segment |
 |
| Trace from Site 2 physical router to VM on segment |
Failover/DR scenario:
 |
| Traffic flow through DR site |
The primary site has failed.
So the physical routers in primary site are down.
Edges in primary site are also down.
Now the DR only Tier 1 Gateway has to be connected to Tier 0 Gateway of Site 2 to influence traffic flow through Site 2.
 | |
| Tier 1 Gateway is connected to Tier 0 Gateway of Site 2 |
 |
| Trace from loopback on physical router of Site 2 to VM on segment |
Now verify the traffic flow by sourcing traffic from loopback network on physical router of Site 2.
 |
| Workload VM can reach loopbacks of physical routers in Site 2 |
No comments:
Post a Comment